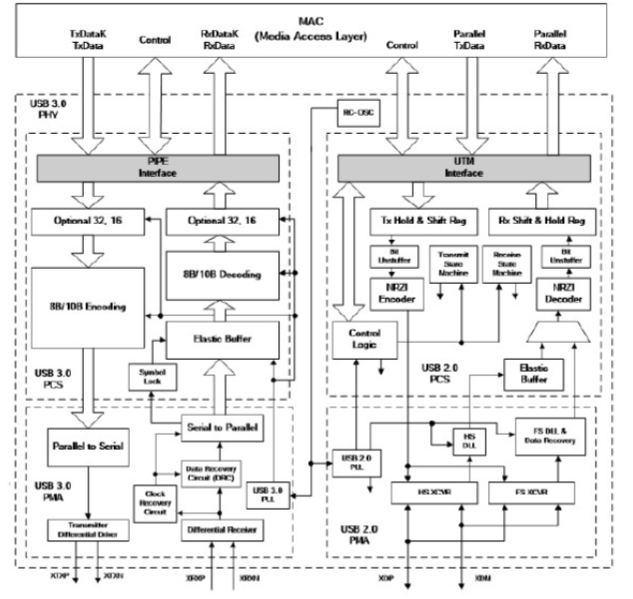
For auxiliary devices, a Universal Serial Bus (USB) transceiver is offered. The PHY complies with the requirements of UTMI, USB 2.0 PIPE, and USB 3.0 (USB SuperSpeed). The USB3.0 PHY IP transceiver is designed to consume little power and take up little space on the chip without compromising speed or data throughput. The USB3.0 PHY IP includes a full on-chip physical transceiver solution with Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) protection, a built-in self-test module with inbuilt jitter injection, and a dynamic equalization circuit to provide comprehensive support for high-performance designs. Several IP sources are supported by the USB3 MAC layer through the shared PHY interface (PIPE). Internal test monitoring and jitter are reduced by using constant power, built-in Jitter Injection Output, built-in Self-Test, and approved change of analogue circuit characteristics.
Deliverables
Integrated Circuit Layout with Layer Configuration
Design Views for Placement and Routing in LEF Format
Liberty Standard Cell Library
Verilog Representation of Circuit Behavior
SDF-Annotated Netlist for Timing Analysis
Design Guidelines and Best Practices for Layout
Validation Reports for Layout Consistency and Rule Adherence